
Anabia Akbar
Climate change refers to long-term changes in weather patterns and temperature. Such changes can be natural, due to changes in the sun’s activity or large volcanic eruptions. But since the 1800s, human activities have been the main driver of climate change, primarily due to the burning of fossil fuels like coal, oil and gas.
Burning fossil fuels generates greenhouse gas emissions that act like a blanket wrapped around the Earth, trapping the sun’s heat and raising temperatures. The main greenhouse gasses that affect the climate include carbon dioxide and methane.
IMPACTS OF CLIMATE CHANGE
Rising Temperatures
Global temperatures are increasing, leading to more frequent and severe heat waves. As greenhouse gas concentration rises, so does the global surface temperature. The last decade,2011-2020, is the warmest on record. Since the 1980’s, each decade has been warmer than the previous one.

The warming trend affects agriculture, human health, and water resources, increasing the risk of heat-related illnesses.
Extreme weather Events
Climate change intensifies, extreme weather events such as floods, cyclones, droughts and wildfires. These events cause widespread destruction, displacement of populations, loss of lives, and economic destruction.
Melting Ice and Rising Sea Level
The warming climate causes glaciers and polar ice caps to melt, contributing to rising sea levels. As temperatures rise, glaciers melt faster than they accumulate new snow. As these ice sheets and glaciers melt, the water eventually runs into the ocean, causing sea level to rise. Certain glaciers and ice sheets are particularly vulnerable.
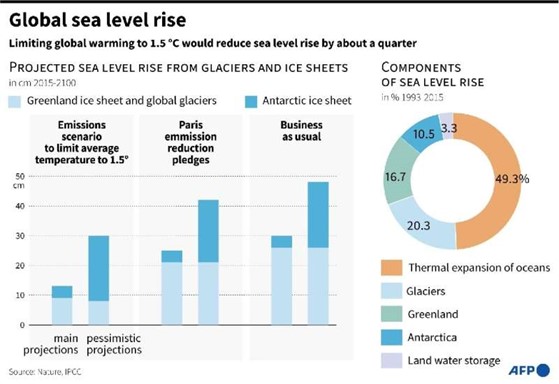
Global warming has caused them to be less stable, to move faster towards the ocean, and to add more ice into the water.
Agriculture and Food Security
Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns affect crop yields, food production, and livestock.

Certain crops are climate-sensitive in Pakistan such as rice, vegetables, cereals, spices and other grains. Rising temperatures and changing rainfall result in the form of shortage of water, which further leads to problems of food security due to low productivity, especially in the cropped food sector.
Health Risk

Climate change contributes to the spread of infectious diseases, affects air and water quality, and exacerbates health problems due to extreme heat. Environmental hazards like water and air pollution, extreme weather, or chemical exposures can affect human health in a number of ways, from contributing to chronic diseases like cancer or acute illnesses like heat exhaustion.
Biodiversity Loss
Habitats are being altered or destroyed due to changing climates, affecting plant and animal species. Many impacts of climate change including drought, bushfires, storms, ocean acidification, sea level rise and global warming affect biodiversity.

Loss of biodiversity can lead to land degradation, effects on water supply and changes in farming productivity.
Economic Impact

Climate change poses significant economic risks, affecting industries such as agriculture, tourism, insurance, and infrastructure. Climate change impacts our society by disrupting the natural, economic and social systems we depend on. This disruption will affect food supplies, industry supply chains and financial markets and harm global development.
___________________________
The author is a student of Mass Communication from Women University Multan.

